Infrastructure Priority List
Search the Infrastructure Priority List
The Infrastructure Priority List is changing in line with amendments to the Infrastructure Australia Act 2008. Find out more here.
proposals found with keywords: Nil and filters: All
- List View
- Map View
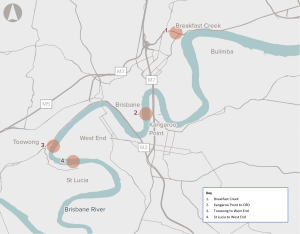
Opportunity to address challenges associated with congestion, forecast population growth and geographical limitations by improving active transport networks across the Brisbane River.
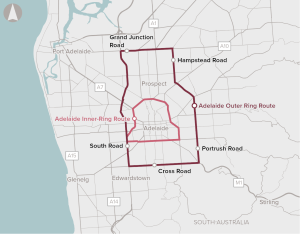
Increasing population growth in Adelaide is expected to increase congestion and travel times in the suburbs surrounding inner-Adelaide, to the CBD, as well as impact freight productivity and safety for pedestrians and cyclists.
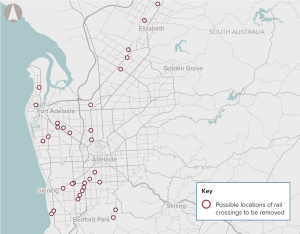
There are 127 at-grade level crossings of the road and rail network in Adelaide. Level crossings can lead to delays and safety problems as trains, cars, buses, trucks, cyclists and pedestrians cross paths. Pedestrian and vehicle collisions and boom-gate strike crashes can result in injuries or fatalities, as well as property damage and delays on transport networks.
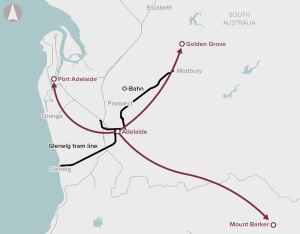
The 2019 Australian Infrastructure Audit found that the performance of urban roads and urban public transport in Adelaide is a key challenge for South Australia.
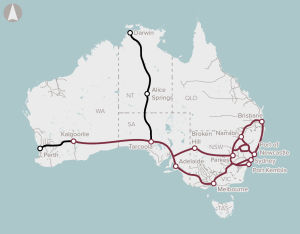
Delivery of a wireless satellite communications-based train control system, that will replace line-side signalling to improve rail capacity, transit times and rail safety.
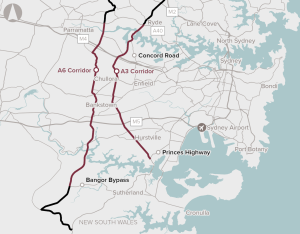
A range of interventions aimed at reducing capacity constraints on the A3 and A6 corridors.
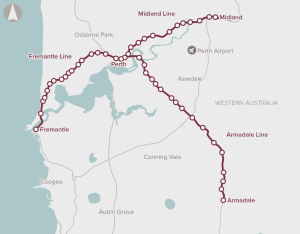
The Armadale, Midland and Fremantle rail lines are known as Perth’s ‘heritage lines’. They were built in the 19th Century and service well-established suburbs around Perth. The capacity of the heritage lines is insufficient to accommodate future growth. This will lead to crowding, passenger discomfort, unreliability and road congestion if people choose not to travel by rail.
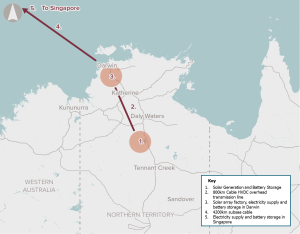
The public outcomes to the Australian community from the Australia-Asia PowerLink proposal are highly positive. The benefits are premised on the proposal being largely developed on a commercial basis with private funding. The realization of benefits is dependent on the proponent achieving contracted energy supply.
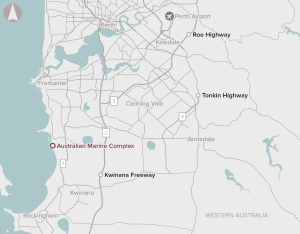
The AMC is an integrated marine and industrial fabrication complex established to support the construction, development and maintenance of major projects and assets in the oil and gas, mining and shipbuilding industries. The existing complex is home to over 150 businesses. However, there is limited infrastructure capacity at the complex and the common user facility to support growing demand.
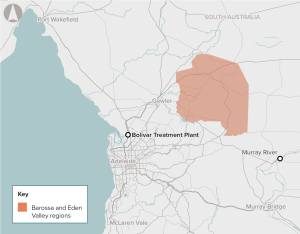
The River Murray is currently the major source of irrigation water to the Barossa Valley Region. Smaller volumes of groundwater are available, although the quality in some areas is not fit-for-purpose or sufficient to meet increasing industry demand.
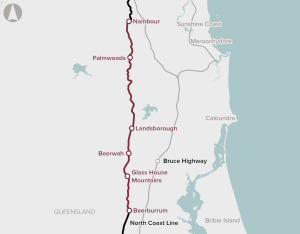
Duplication of a 20 km section of track from Beerburrum to Landsborough, as well as passing loop extensions and station upgrades between Landsborough and Nambour, to improve the efficiency of passenger and freight rail services.
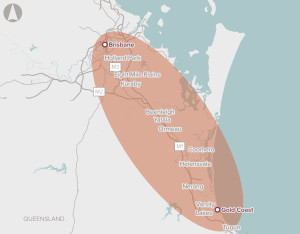
A 10-year, network-wide program for upgrades to transport infrastructure in the corridor, including road, rail, cycling and bus improvements.
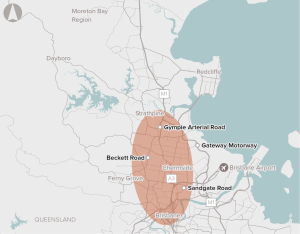
Capacity for Brisbane's northern transport corridors to support residential growth in northern Brisbane, combined with employment growth primarily in the Brisbane CBD.
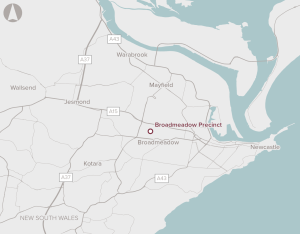
There is an opportunity to redevelop an existing sports and entertainment precinct five kilometres from the Newcastle CBD.
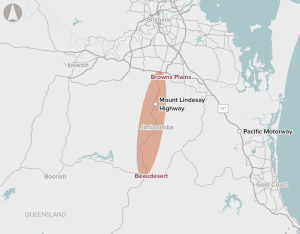
Capacity and safety issues along the corridor between Browns Plains and Beaudesert.
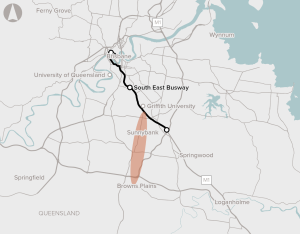
Improving public transport connectivity along the 14km major transport corridor between Browns Plains and the South East Busway.
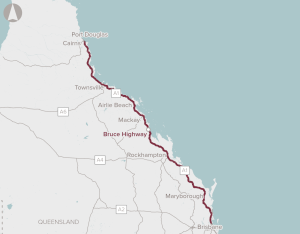
A broad package of works to progressively upgrade priority sections of the Bruce Highway to address specific capacity constraints, flood resilience and safety concerns.
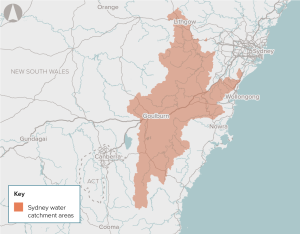
The proposal is for a mix of infrastructure and non-infrastructure responses (such as demand management) to efficiently meet agreed service standards for water security in Australia’s towns and cities.
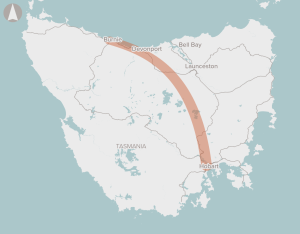
Development of a Burnie to Hobart Freight Corridor Strategy, which will prioritise areas for investment along the corridor, with a focus on improving intermodal freight productivity
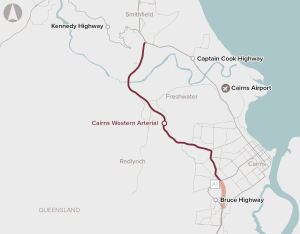
The Cairns Western Arterial Road provides important access for commuter, tourism and freight traffic. Approximately 42,000 vehicles use the busiest sections of the road each day, resulting in heavy congestion and queuing on the undivided sections of the road and at its intersections.
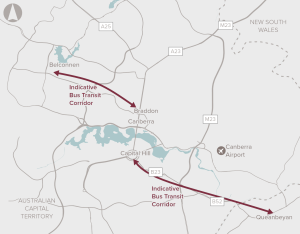
An integrated transport solution through developing bus transit corridors between Belconnen and Queanbeyan to central Canberra.
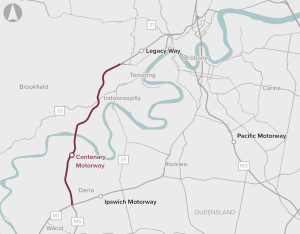
Improve capacity along the Centenary Motorway to support the rapid population growth of Brisbane's Western Corridor.
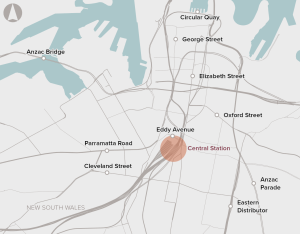
Upgrades to rail and station infrastructure to support passenger movement and interchange
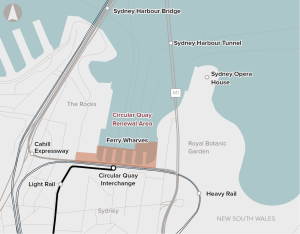
The proposal demonstrates alignment with local and state government strategies and priorities, and embeds a place-based, holistic approach to investment that activates the broader precinct. We consider the economic appraisal to provide a thorough assessment of the economic merits of the proposal, and that, on balance, it is expected to deliver net economic benefits to society.
The proposal is for a proactive infrastructure strategy in advance of the inundation risks materialising. Involving engagement with all levels of government, the strategy will need to consider which areas should be protected for continued use, modified to accommodate floods, or withdrawn from altogether.
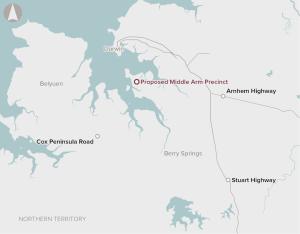
There are several manufacturing businesses that could add value to the Northern Territory’s mining products such as downstream gas processing and high-value minerals processing and refinement. There is insufficient marine infrastructure and serviced land available adjacent to the existing Darwin port to enable these opportunities.
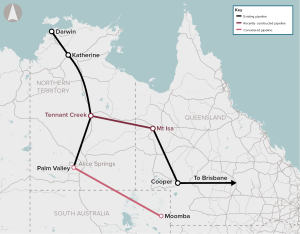
The initiative would develop infrastructure to connect northern and/or western Australian gas reserves to the eastern gas markets
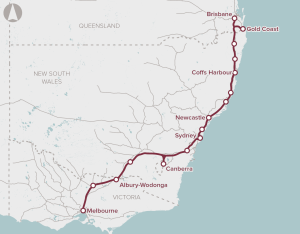
Preserve the corridor for a high speed rail link between Melbourne, Sydney and Brisbane.
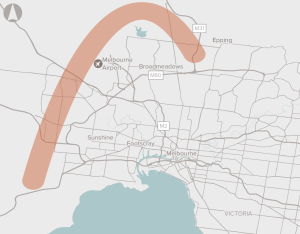
Preserve the corridor for the Outer Metropolitan Ring Road and E6 in Melbourne.
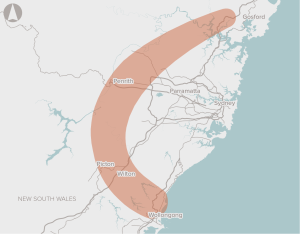
Conducting a planning study to identify a preferred alignment for a multi-modal transport corridor comprising a motorway, a north-south freight rail line, and where practical, passenger rail, and to preserve the preferred corridor.
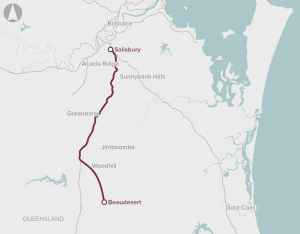
Preservation of the corridor between Salisbury and Beaudesert in Brisbane's south-west region for the potential future development of passenger rail services.
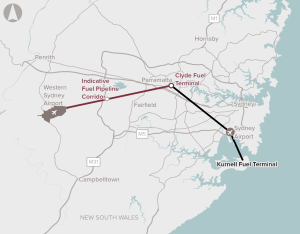
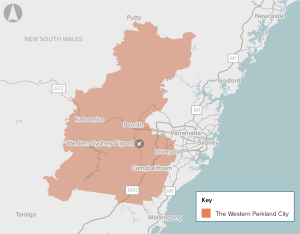
Identify and preserve a corridor for a fuel pipeline connection between the Sydney fuel pipeline network and Western Sydney Airport.
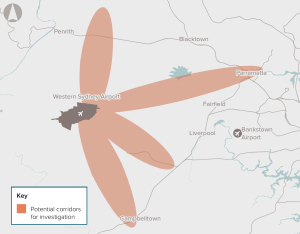
Preserve the rail corridor connecting the Western Sydney Airport to the Sydney rail network.
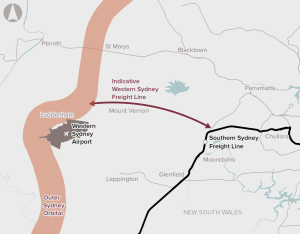
Reduce growth in truck movements on the Sydney road network and reduce delays to freight trains on the main Western Line through preservation of the corridor
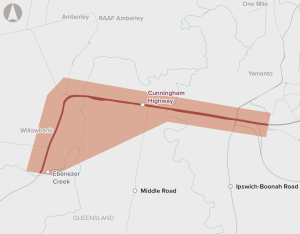
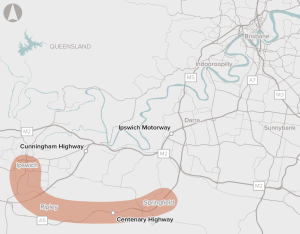
Upgrades to a 4.75 km section of the Cunningham Highway between Warwick Road at Yamanto and Ebenezer Creek, including the Amberley Interchange.
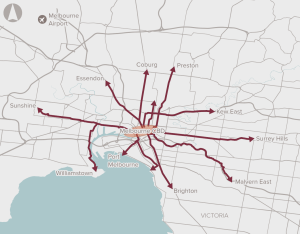
The proposal involves the provision of dedicated cycling infrastructure for key routes in Inner Melbourne to reduce congestion and improve safety and health outcomes.
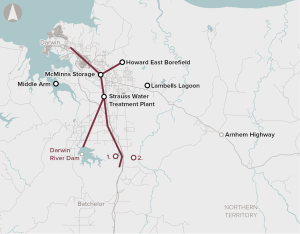
Ensure secure water supply to support further urban, industrial and/or agricultural development in some parts of the country.
Providing digital infrastructure would enable the adoption of technologies that reduce travel times, reduce resource use and emissions, improve health and provide more ways for community members to access up to date information about services and developments in their city.
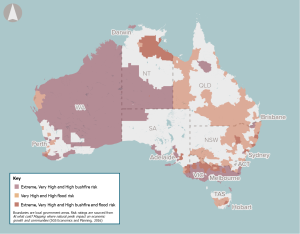
As the frequency and severity of natural disasters increase due to climate change, early warning systems present an opportunity to improve the safety and wellbeing of communities in high-risk zones.
The proposal is for infrastructure improvements which enable larger vessels access to Australian ports on the east coast. This could require channel deepening at existing ports, development of new port locations and enhanced land-side access infrastructure at ports.
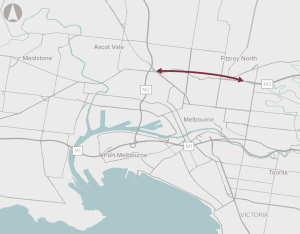
Improve the connection between the Eastern Freeway and CityLink.
Enabling digital health technologies in regional and remote areas of Australia can improve equity of access and outcomes, reduce costs associated with delivering health care and reduce avoidable hospitalisations.
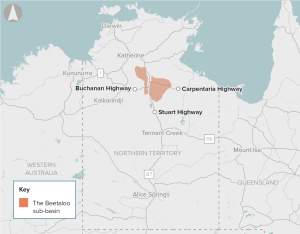
The Beetaloo Sub‑Basin has been identified by industry as containing a significant quantity of gas that could be within economically feasible depths to extract.
There is a significant opportunity to develop supply chains in Australia to meet potential demand in domestic and export markets.
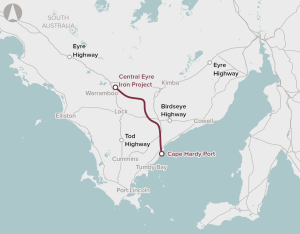
Development of a deep water port at Cape Hardy, and a 148 km heavy-haul, standard gauge rail connection between the mine and the port.
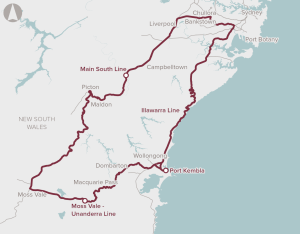
Improvement in rail freight access to Port Kembla, potentially through enhancements to existing lines, or the future development of an alternative rail alignment to the port.
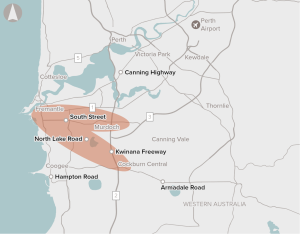
Limited high priority public transport services to connect employment centres and tourism hubs with major residential and commercial developments.
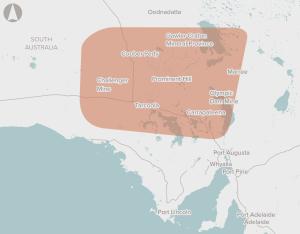
Building and operation of a 350 km railway in the Gawler Craton province, linking to the existing interstate rail network. Future connections to other potential mining plans will be possible.
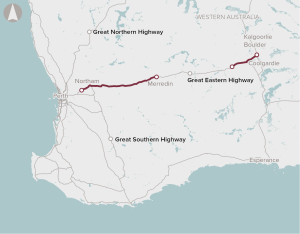
Deteriorating road conditions, increasing travel times, aging bridges and relatively high road maintenance costs on the Great Eastern Highway.
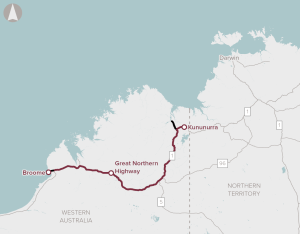
The proposal involves improvements to address safety, pavement and bridge strength and width, culvert rehabilitation and flooding resilience on sections of the Great Northern Highway between Broome and Kununurra. The proponent has demonstrated that a program of road upgrades to the existing highway is the most appropriate response to the problems and opportunities they have identified.
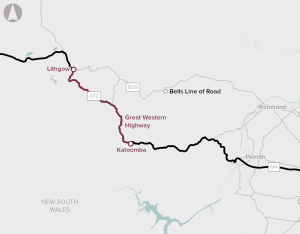
The proposal is to complete the duplication of the Great Western Highway. Over 100 km of the highway has been duplicated so far, leaving a 33 km gap between Katoomba and Lithgow.
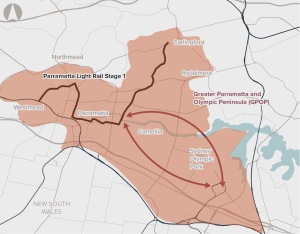
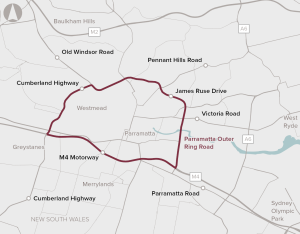
Poor connectivity to and from precincts in Greater Parramatta and the Olympic Peninsula, limiting ease of movement.
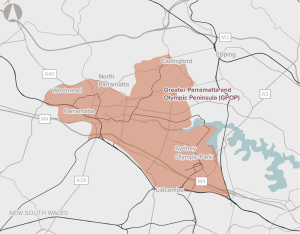
Opportunity to co-ordinate delivery of infrastructure to support sustainable growth in Greater Parramatta and the Olympic Peninsula.
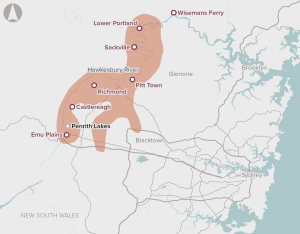
The Hawkesbury–Nepean Valley Integrated Flood Management Strategy presents a series of proposals and investments to reduce flood risk in the valley
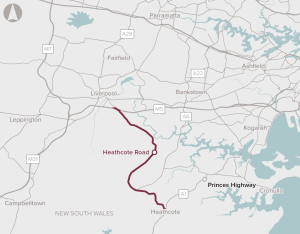
Heathcote Road is a 24.5-kilometre arterial road connection between the M5 Motorway and A1 Princes Highway. The current road capacity and design is leading to congestion, poor reliability and safety issues, particularly around key intersections. Several sections of Heathcote Road have minimal overtaking opportunities.
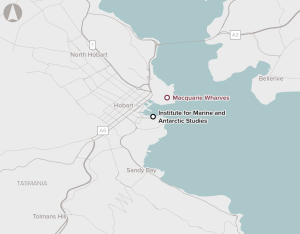
In its existing condition, the port cannot accommodate the Australian Antarctic Division’s new purpose-built icebreaker, RSV Nuyina. It also cannot accommodate the Oasis passenger cruise vessels, impacting on tourism.
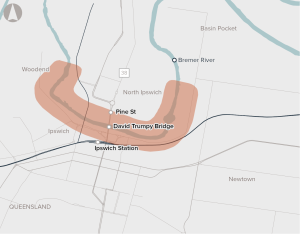
Strong forecast population growth and a single river crossing is expected to place increasing pressure on the transport network in Ipswich.
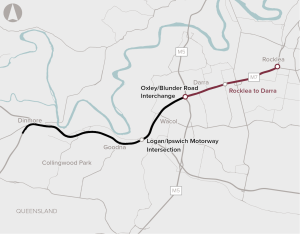
Improvements to road capacity along the Ipswich Motorway between Rocklea and Darra by providing additional lanes, upgrades of bridges and ramps and other provisions.
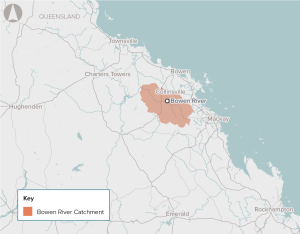
A constrained water supply is limiting the growth of agricultural, industrial and mining productivity in and adjacent to the Bowen Basin. Increasing the water supply can unlock additional agricultural land and facilitate a more robust water trading market with potential flow-on price reductions for mining and industrial water users.
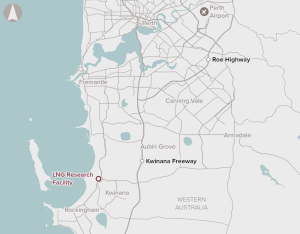
The proposal is for a national facility to develop and test new technologies with the potential to improve operational performance, as well as potentially increase process reliability and reduce production costs.
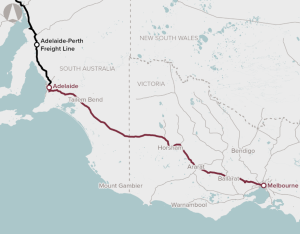
The Melbourne to Adelaide freight rail corridor cannot carry double-stacked containers. This increases costs for operators and impacts on freight rail between Melbourne and Adelaide, and also to Perth.
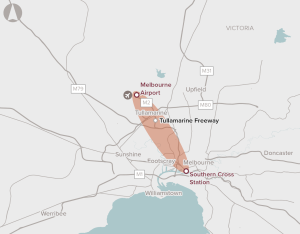
Develop options for increasing public transport capacity to Melbourne Airport.
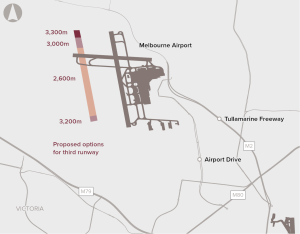
A third runway to meet increased demand at Melbourne Airport, which is expected to reach capacity during peak periods between 2018 and 2022.
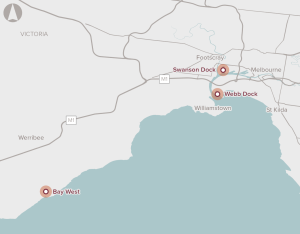
Planning for and construction of additional container terminal capacity in Melbourne to cater for predicted increases in containerised freight volumes.

Various upgrades to the Melbourne–Geelong rail line to enhance capacity, including electrification of the line and duplication of the existing single track pair.
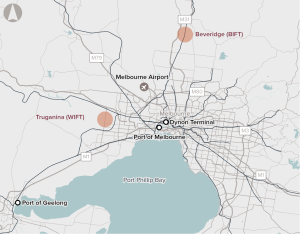
Existing intermodal terminal capacity in Melbourne is unable to service Inland Rail trains (1800m long, double-stacked).
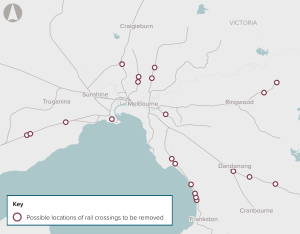
Removal of priority level crossings to deliver a more reliable, convenient, productive and safer transport system in Melbourne.
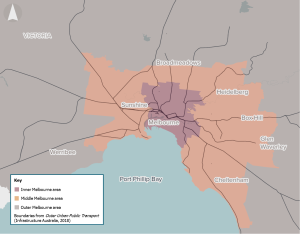
Melbourne’s monocentric urban form is constraining the economic potential of Melbourne’s middle and outer suburbs.
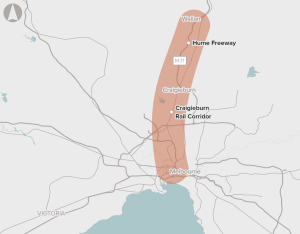
Develop options to address demand for transport services in Melbourne's outer northern suburbs.
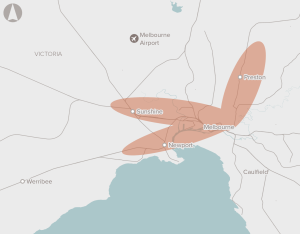
Improvements to Melbourne's rail network capacity.
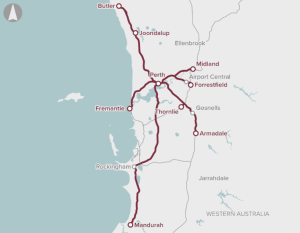
Perth’s existing signalling and train control systems.
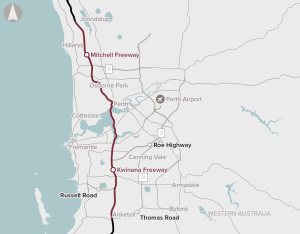
Widening the Mitchell and Kwinana Freeways and implementing Intelligent Transport System technologies.
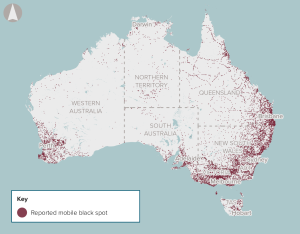
The proposal is to improve the availability and quality of mobile services in certain regional and remote areas.
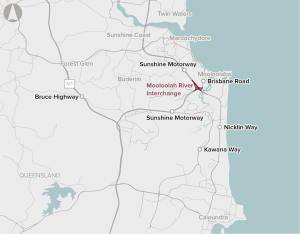
Traffic demand is exceeding the capacity of the Mooloolah River Interchange and the surrounding road network during peak periods.
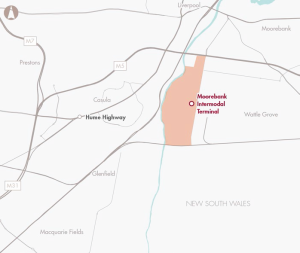
A package of inter-related road infrastructure improvements to increase network efficiency and improve access to the Moorebank Intermodal Terminal
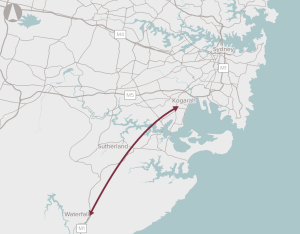
Deliver a motorway connection from the M1 at Waterfall to the Sydney motorway network.
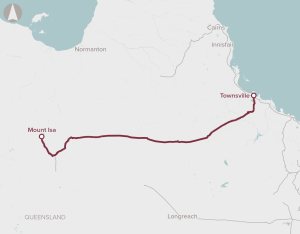
Enhancements to western sections of the Mount Isa to Townsville Rail Corridor and construction of a new 6.5km Townsville Eastern Access Rail Corridor.
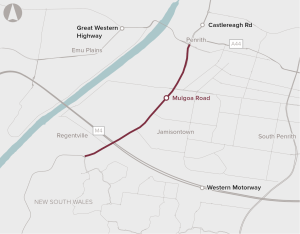
High levels of congestion and safety risks on Mulgoa Road in Western Sydney.
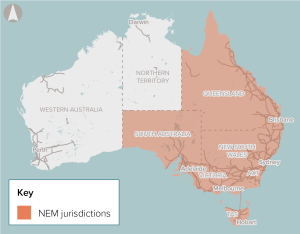
The National Electricity Market (NEM) will require significant investments in dispatchable energy storage to support growing renewable energy generation and the future retirement of coal-fired generators.
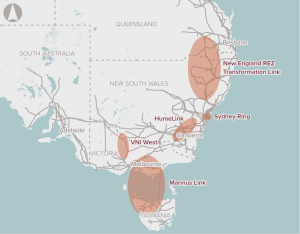
Improved connections between regions of the National Electricity market use of resources across the NEM in the medium term and ensuring system reliability and security in the longer term.
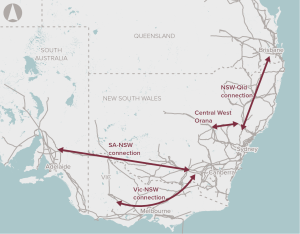
Improve interconnections between NEM regions to make better use of existing assets.
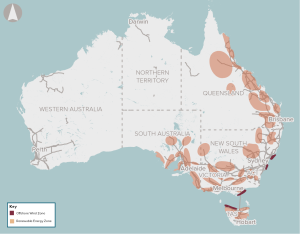
The National Electricity Market (NEM) will require significant new grid-scale renewable energy generators to replace retiring thermal generation facilities.
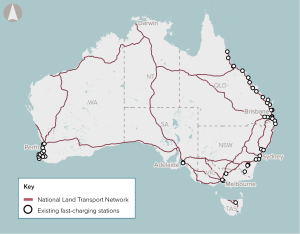
Developing a network of fast-charging stations on the national highway and policies and regulation to support charging technology adoption.
The proposal is for addressing the road maintenance backlog across local, state and national roads.
A program of works focused on addressing capacity constraints and improving service levels on urban and regional rail networks.
A portfolio of works focused on addressing congestion on urban road networks with comparatively high public transport and freight use across multiple corridors in Australian cities.
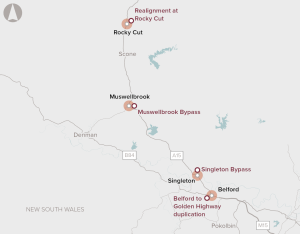
A number of potential developments, including bypasses of the towns of Singleton and Muswellbrook, and intersection upgrades.
The current limitations of the terminal and runway impacts inbound and outbound flights to domestic destinations and restricts access to international destinations in Oceania. This leads some passengers to commute to and from Sydney Airport for air travel.
A package of improvements to passenger rail services between Newcastle and Sydney and Wollongong, including operational and fleet improvements, grade improvements and a new rail crossing of the Hawkesbury River and Illawarra Escarpment.
Improvement to several sections of the highway to support safe Higher Productivity Vehicle access, and improve safety and reliability
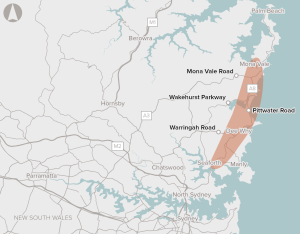
The cost of congestion and poor access to and from Sydney’s Northern Beaches is significant.
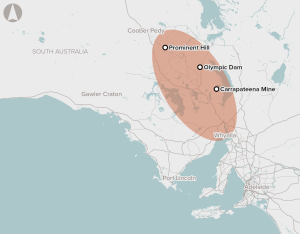
Mines in northern South Australia rely on groundwater from the Great Artesian Basin and other smaller local aquifers. This water is expensive to extract, as harvesting can be slow in low-pressure zones, and salinity and other water quality issues can affect its use.

Additional tracks from West Ryde to Rhodes and from Thornleigh to Hornsby to support the future growth of rail freight movements.

There is an opportunity to improve freight and logistics infrastructure on the Darwin to Tarcoola rail line in the Northern Territory to enable private investment and development of the NT's rich resource base in gas, minerals, rare earths and solar irradiance.

The Northern Territory Remote Power System Strategy set a target for 70% renewable electricity generation for Indigenous Essential Services communities. This is expected to improve resilience, flexibility, reliability, amenity and sustainability of power infrastructure in remote Aboriginal communities of the Northern Territory.
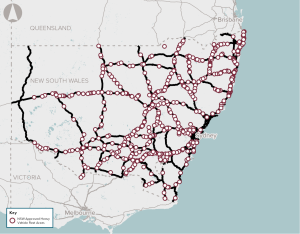
Insufficient or inadequate infrastructure to allow drivers of heavy vehicles to stop and rest across NSW.
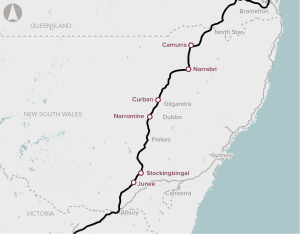
Ensuring interoperability between the Country Regional Network and Inland Rail to maximise productivity and efficiency of freight movements from regional NSW to domestic and export markets.
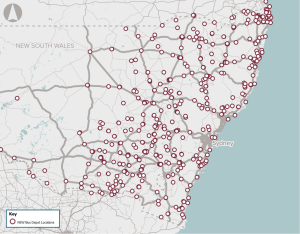
Greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and noise pollution associated with diesel-powered public buses in NSW.
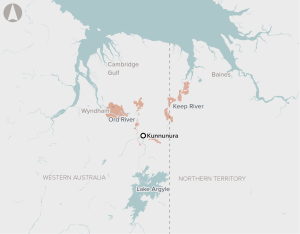
Opportunity to upgrade and extend irrigation channels to expand irrigated crops in the Ord River Irrigation Area in North-West Western Australia and the Keep River Plains in North-East Northern Territory.
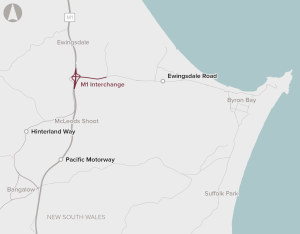
The intersection of M1 Pacific Motorway and MR545 is the key interchange to Byron Bay on the NSW North Coast. Commuter and tourism traffic is leading to growing congestion at this intersection, particularly during peak times. While variable speed signs have been implemented to manage congestion, there is an increasing risk of vehicle crashes due to the excessive congestion and queueing.

Options analysis for the section between Daisy Hill and Loganholme aligns with the requirements of the Infrastructure Australia Assessment Framework.
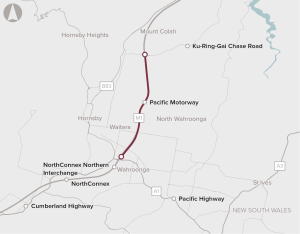
Extreme congestion on the M1 Pacific motorway between the existing North Connex portal and Mt Colah.
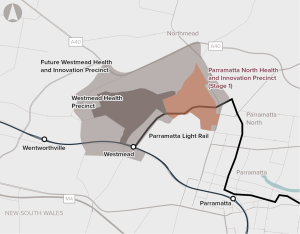
Opportunity to redevelop Government-owned land in Parramatta North, capitalising on the redevelopment of Westmead and the Parramatta Light Rail.
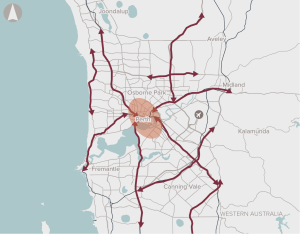
Worsening road congestion, high private vehicle use and a lack of dedicated active transport connections that link key strategic centres in Perth.

Construction of an additional runway at Perth Airport to provide capacity needed to meet increasing demand.
The proposal is for a program of water sourcing and water demand management interventions. This could include a mix of more conventional water sources, as well as more innovative reuse and recovery options, to provide additional sources of climate-independent potable water.
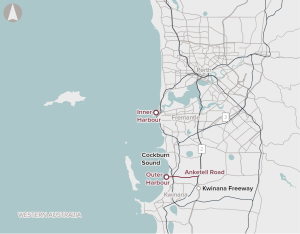
Investigation, planning, and potentially corridor and site preservation for additional container terminal capacity to accommodate future demand in Perth.

There are 30 level crossings on Perth’s electrified passenger rail network, which services 72 stations across five lines. Level crossings provide important connectivity for vehicles, cyclists and pedestrians across train lines, but also result in road congestion and safety risks.
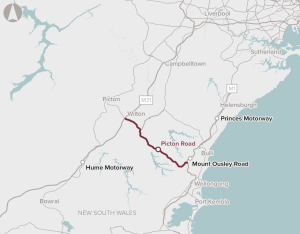
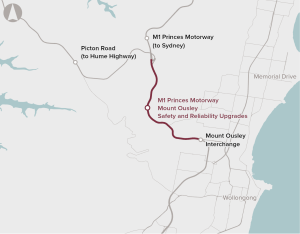
Upgrade Picton road to improve the connection between The Princes and Hume Highways near Mount Ousley.
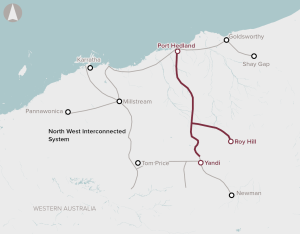
Limited energy transmission and storage infrastructure across the Pilbara in Western Australia.
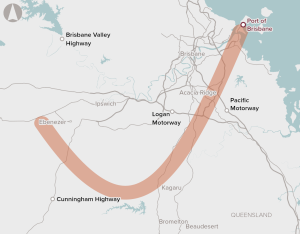
Improve connectivity between the Port of Brisbane and freight terminals in the Brisbane region.
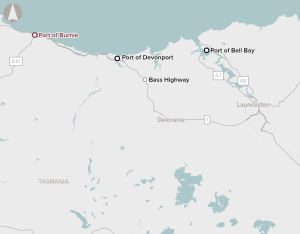
Port capacity and infrastructure at Port of Burnie, on the north coast of Tasmania, is limiting export opportunities.
Port of Burnie cannot accommodate vessels larger than Handymax size, which carry less than 60,000 tonnes. These vessels are too small to service the supply chain. The export terminal space at the port is limited and not fit‑for‑purpose, and multi-commodity logistics infrastructure does not meet the ports requirements.
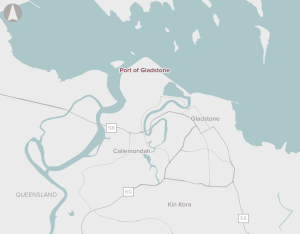
A range of activities, such as channel management to increase export capacity, upgrades to road and bridge infrastructure servicing the port, and new rail infrastructure to provide direct connections.
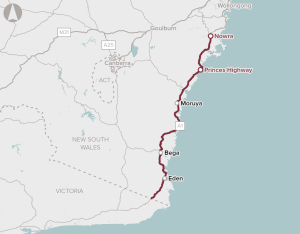
The proposal is for a program of works to make the corridor safer, and more efficient and accessible.
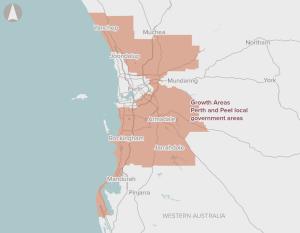
There is limited provision of regional-level sporting facilities in the outer metropolitan areas of Perth, reflecting past undersupply that has not kept up with high population growth.
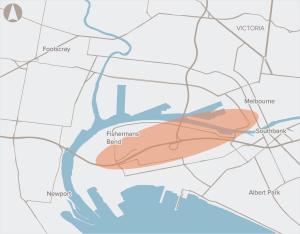
A high capacity, rapid transport link connecting Fishermans Bend with the Melbourne CBD.
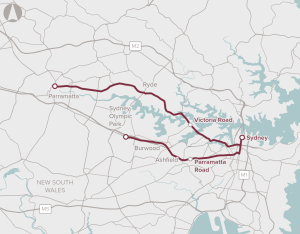
Provision of high-capacity, on-road bus transport to improve connectivity along priority corridors.
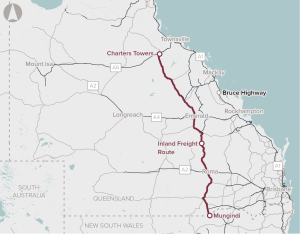
Capacity and safety improvements on Queensland’s Inland Freight Route, from Mungindi (at the New South Wales border) to Charter Towers in North Queensland.
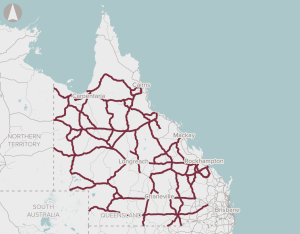
The proposal proposes a strategy that prioritises investment based on the goals of improving productivity and safety on regional Queensland roads, and sustaining regional communities. The proposal includes improvements to address safety, surface issues, flooding, bridge strength and width, road alignments, widening and pavement sealing.
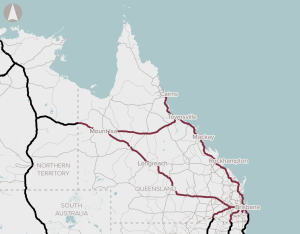
The proposal is for a structured program approach to addressing the maintenance backlog for the NLTN in Queensland.

That make up a disproportionate amount of crashes on Queensland's road network.
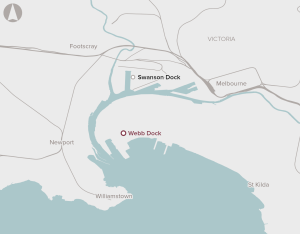
The number of containers handled by the Port of Melbourne is forecast to grow from 3 million twenty-foot equivalent container units (TEUs) in 2019 to close to 9 million TEU by 2050. The majority of this growth in containers will need to be delivered at Webb Dock. However, with the existing infrastructure, all freight to and from Webb Dock is carried by road. This results in increased congestion on the surrounding road network.
This initiative complements the national High Priority Initiative for Regional road network safety improvements. It involves treatments such as sealing shoulders, wide centre lines and audio tactile line marking to attain a safer road cross section on the State’s Highway and Main Roads regional and rural road network.
Introduction of modern road safety infrastructure technology and features, to improve road safety at high-risk locations.around NSW.
During severe natural disasters, regional and remote communities are often isolated due to corridor closures on the National Land Transport Network (NLTN).
A national program of works to improve safety on regional roads.
Regional airstrips.
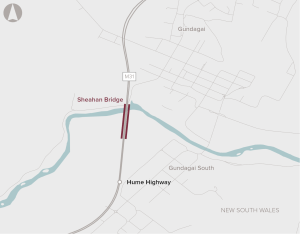
Strength limitations on the northbound Sheahan Bridge at Gundagai are constraining High Productivity Vehicle movements on the Hume Highway.
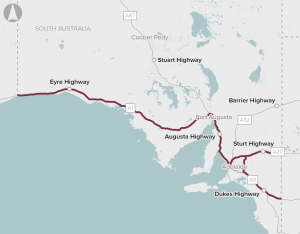
The realignment of the Sturt Highway through the Truro Hills, including a bypass of the town of Truro, to improve safety and allow use of High Productivity Vehicles on the highway.
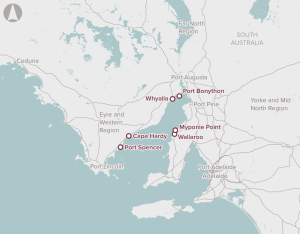
Identification of potential options for the development of bulk commodity port capacity in the Spencer Gulf region.
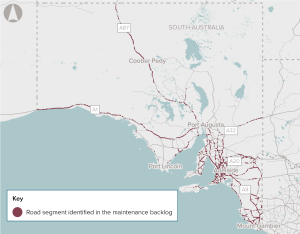
There is a large and increasing backlog of maintenance on the national and state-owned roads in South Australia, which is increasing costs for road users.
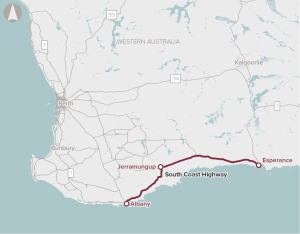
The proposal involves upgrades to the South Coast Highway between Albany and Esperance.
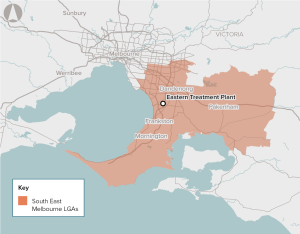
Climate change, population growth and ageing assets present potential longer-term water security problems for Melbourne. Climate-independent water supply sources can help address the problem. Melbourne’s Eastern Treatment Plant produces over 130 billion litres of recycled water each year. Currently, about 95% (123 billion litres) of this water is treated and safely discharged into the Bass Strait.

Existing intermodal terminals in SEQ are restricted in their ability to service Inland Rail trains (1800m long, double-stacked).
South East Queensland’s Citytrain network includes 65 level crossings. Most of these level crossings are in urban environments, which can lead to congestion and safety issues.
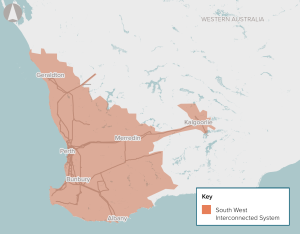
The proposal involves network, generation and storage investment in the SWIS.
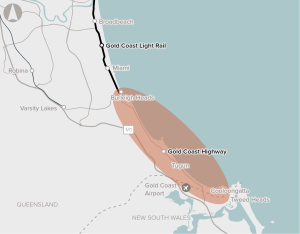
Limited route choice and public transport options, as well as high car dependency will exacerbate existing congestion with population growth.
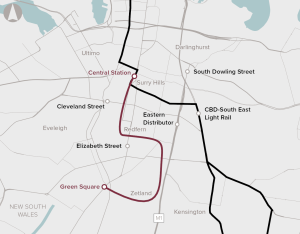
Provide high-capacity and rapid transport link between Sydney CBD and unserved parts of Green Square.
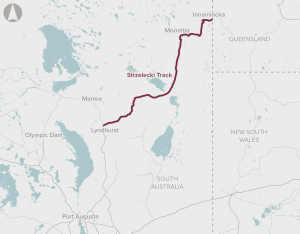
Upgrades to 426 km of the Strzelecki Track between Lyndhurst and Innamincka, and 26 km of the Nappa Merrie Access Road
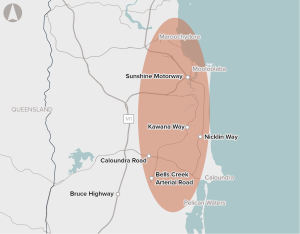
Strong population growth, a constrained road network, and limited transport options are contributing to congestion between Caloundra and Maroochydore.
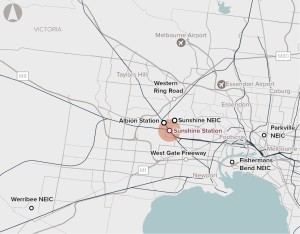
Opportunity to redevelop Sunshine Station and the surrounding precinct as a major future PT interchange linking Melbourne Airport, the CBD and regional Victoria.
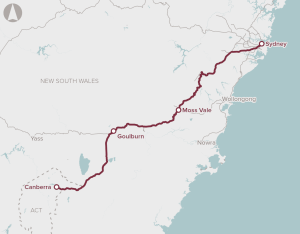
The opportunity is for a range of potential upgrades to enable faster rail services between Sydney and Canberra to improve the customer experience, increase productivity and provide a competitive alternative to driving or flying.
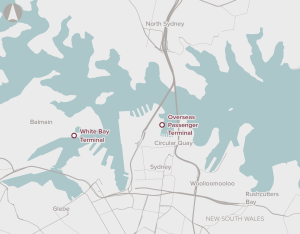
Reduce cruise terminal capacity constraints to support growth of the Australian tourism industry.
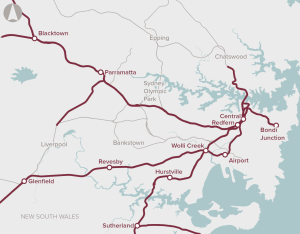
Solutions to accommodate the strong future growth in rail patronage in the Sydney basin.
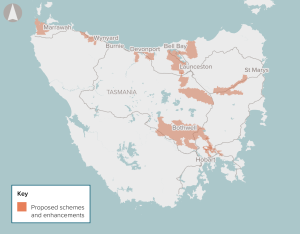
Investment in rural water storage and delivery infrastructure to enable large-scale, multi-user irrigation schemes in rural areas in Tasmania.

Rationalise existing sewage treatment plants and upgrade and operate a reduced number of sewage treatment plants in Hobart, Launceston and Devonport.
The initiative is for a mix of infrastructure and non-infrastructure responses (such as demand management) to efficiently meet agreed service standards for water security in Australia’s towns and cities.
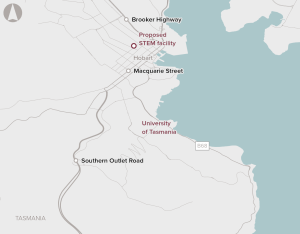
Relocation of the University of Tasmania’s Faculty of Science, Engineering and Technology from the existing campus at Sandy Bay to a purpose-built facility for education, research and training in the Hobart CBD.
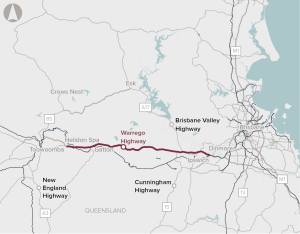
Upgrading the Dinmore to Helidon Spa section of the Warrego Highway to improve road safety, capacity and flood immunity.
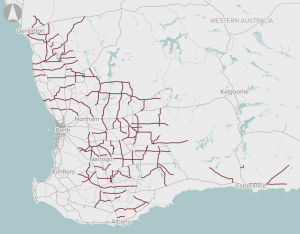
The program is for assessing and prioritising sections of the Wheatbelt Secondary Freight Network.

Increasing coastal erosion and inundation risks across Western Australia.

There is poor access to digital services in the regional and remote areas of Western Australia due to a lack of fit-for-purpose digital infrastructure and low service performance of existing infrastructure.
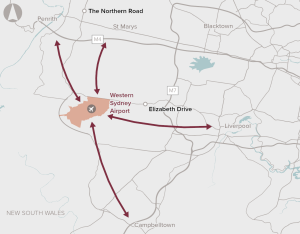
Infrastructure upgrades to support bus connections between the proposed Western Sydney Airport and the nearby centres of Liverpool and Penrith. It does not preclude direct rail access in the future.
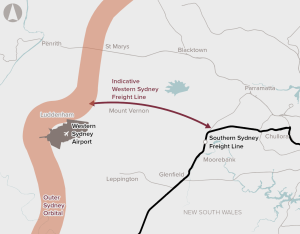
Currently there is no freight rail serving the Western Sydney Employment Area, which is located close to the new Western Sydney International Airport (due to open in 2026).
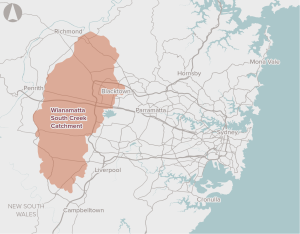
The proposal is to develop the South Creek Catchment in a way that maximises the opportunity for integrated land use and water cycle planning, to enhance the liveability and environmental quality of the area.