Infrastructure Evaluations
proposals found with keywords: Nil and filters: All
- List View
- Map View
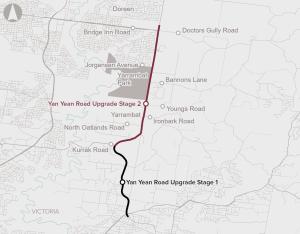
The Yan Yean Road Upgrade Stage 2 will duplicate 5.5 km of Yan Yean Road from Kurrak Road to Bridge Inn Road from two lanes to four lanes.
The proposal supports improved connectivity by linking key suburbs in Melbourne’s north and addressing congestion and safety challenges in a rapidly growing corridor.
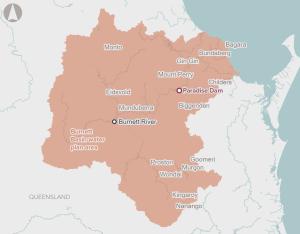
The Paradise Dam Improvement Project aims to restore water security and ensure long-term dam safety in the Bundaberg region by constructing a new dam wall downstream of the existing structure.
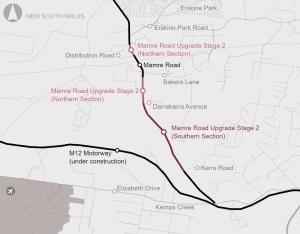
The Mamre Road Stage 2 proposal aims to enhance road capacity of a key arterial road in Western Sydney. The proposal will primarily increase the capacity of the road, whilst improving travel times, reducing transport emissions and delivering better road safety outcomes.
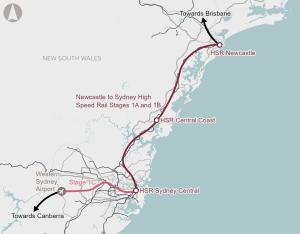
The Newcastle to Sydney High Speed Rail proposal intends to establish an efficient and reliable transport solution between Newcastle and Sydney, one of Australia’s busiest regional corridors.
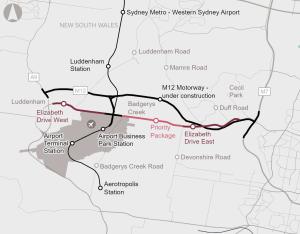
The proposal will enhance the capacity of the transport network by widening Elizabeth Drive from two lanes to four lanes (with future provision for six lanes). The enhancement of this transport corridor includes four bridge replacements and numerous upgraded intersections. Complementing the widening, enhanced public transport and active transport infrastructure is proposed
As a result of the project, resilience of the transport network is…
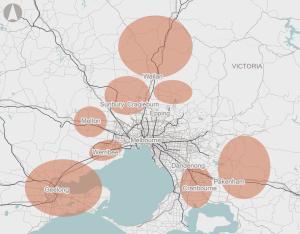
Numerous state Government residential growth corridors have been developed across outer Melbourne and Geelong. This project seeks to evaluate and deliver a range of targeted transport upgrades to increase the capacity of the road network. The detailed evaluation should also consider opportunities for investment in public transport.
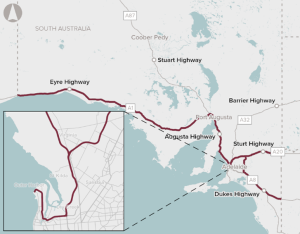
Identification of potential options for upgrades to South Australia’s road network to improve access for High Productivity Vehicles.
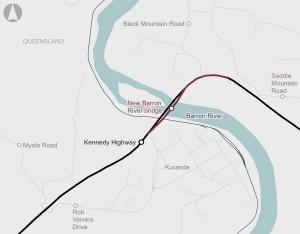
The Barron River bridge is a critical link between Cairns, Kuranda and the Northern Tablelands, supporting daily access for residents, freight and essential services. The existing structure, built in 1963, is experiencing structural deterioration, increasing maintenance needs and safety risks. The business case recommends a new replacement bridge be constructed downstream from the existing bridge.
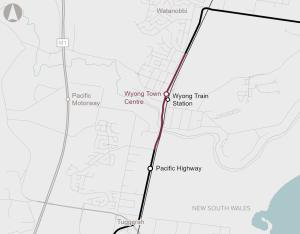
The upgrade aims to improve traffic flow, travel times and safety for all road users, as well as provide for future improvements to the public transport network.
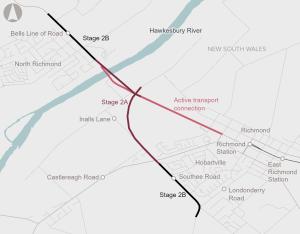
The project aims to reduce congestion and improve flood resilience by constructing a new bridge, upgrading key intersections, and providing a bypass of Richmond. The existing bridge will remain in its current form and be utilised as an active transport connection.
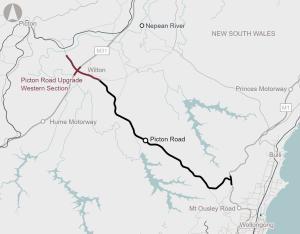
The Picton Road Upgrade (Western Section) involves the upgrade of Picton Road between the Nepean River and Almond Street, Wilton and its interchange with the M31 Hume Motorway.
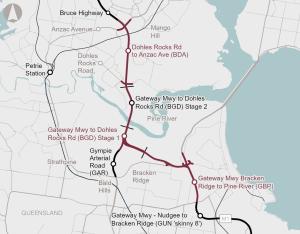
Queensland's Department of Transport and Main Roads has identified upgrades for the Bruce Highway South Corridor to reduce congestion and improve safety and productivity.
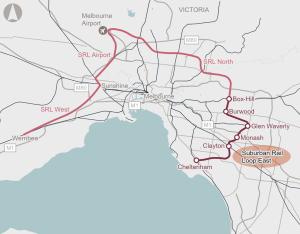
Suburban Rail Loop (SRL) East is the first stage of a proposed mass transit system that will serve Melbourne’s middle and outer suburbs. SRL East includes 26km of twin rail tunnels and six new underground stations between Cheltenham and Box Hill.The proposal aims to reduce travel times, facilitate new housing and connect major employment, health, education and retail areas in Melbourne’s east and southeastern suburbs.
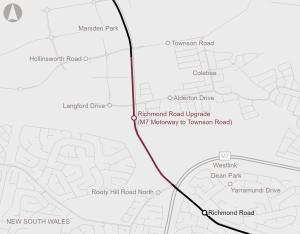
The proposed Richmond Road upgrade between M7 Motorway and Townson Road at Marsden Park as part of North West Growth Centre Road Network Strategy aims to support development in the North West Growth Area.
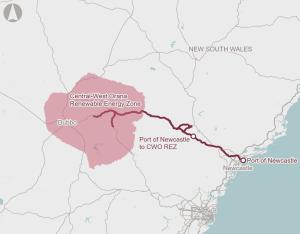
Enabling infrastructure is needed to support the transition to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind farms and batteries, to meet Australian and NSW Government’s emissions reduction targets.
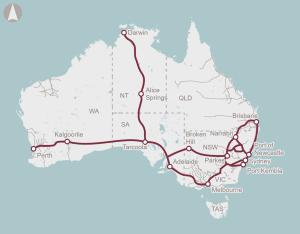
Australia's rail system faces interoperability challenges due to its historical development as separate state-based systems.
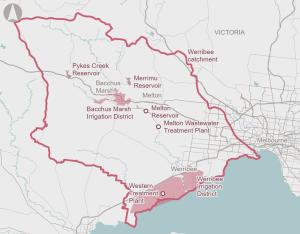
Population growth and climate change are driving greater reliance on more costly sources of water to meet demands for agricultural, urban and cultural uses of water within Victoria’s Werribee River Catchment.
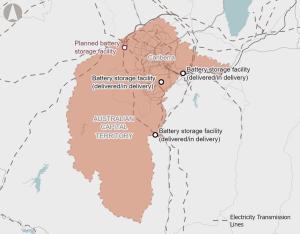
To support growing amounts of renewable energy generation on Australia’s east coast, the National Electricity Market (NEM) requires significant investments in dispatchable energy storage to maintain electricity grid stability and reliability.
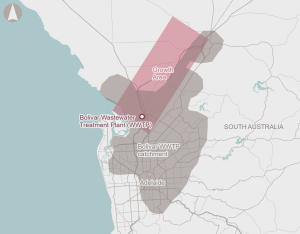
The Bolivar wastewater treatment plant serves 80% of Adelaide’s population and is already operating at 15% above its design capacity due to greater than expected population growth.
The transport sector accounts for a large proportion of Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions. Changes to heavy vehicle technology such as use of High Productivity Freight Vehicles (HPFVs) and Low and Zero Emission Heavy Vehicles (LZEHVs) can contribute to meeting the emission targets for the transport sector.
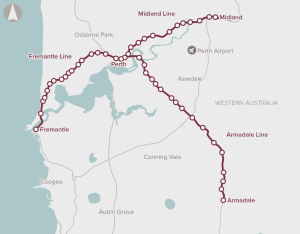
The Armadale, Midland and Fremantle rail lines were built in the 19th Century and service well-established suburbs around Perth. The capacity of the heritage lines is insufficient to accommodate future growth. This will lead to crowding, passenger discomfort, unreliability and road congestion if people choose not to travel by rail.
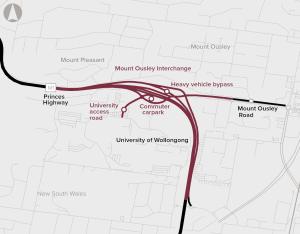
The Mount Ousley Interchange will replace the existing intersection of the Princes Motorway and Mount Ousley Road, improving connectivity, safety and efficiency for those travelling through the gateway to Wollongong.
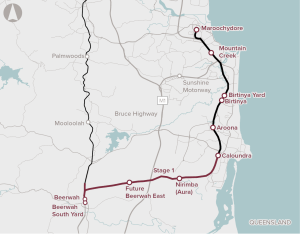
Direct Sunshine Coast Rail Line (Stage 1 – Beerwah to Caloundra)
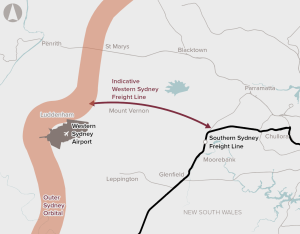
Currently there is no freight rail serving the Western Sydney Employment Area, which is located close to the new Western Sydney International Airport (due to open in 2026).

Recommended for investment to support the Western Australia Government undertake planning activities for the Armadale, Midland and Fremantle rail lines to enhance capacity and accessibility and improve passenger amenity.
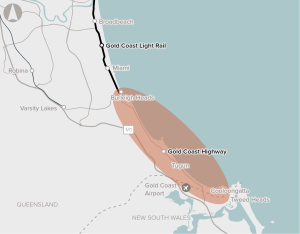
Limited route choice and public transport options, as well as high car dependency will exacerbate existing congestion with population growth.
The M1 Pacific Motorway, Daisy Hill to Logan Motorway proposal aims to address capacity, efficiency and safety issues for the 10-kilometre section of the Pacific Motorway between Daisy Hill and Loganholme through road upgrades and provision of public and active transport infrastructure.
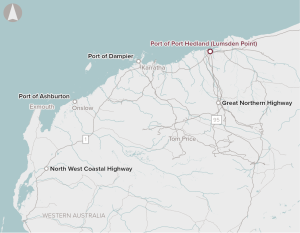
The proposal involves the development of Lumsden Point at Port of Port Hedland, including the provision of an additional deep water general cargo facility in the Pilbara providing for expansion of direct shipping services to the Pilbara.
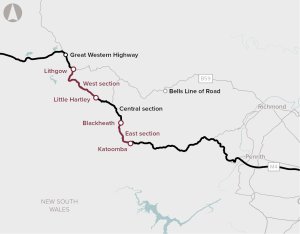
Upgrades to the East and West sections of the Great Western Highway is the first stage of the proposed Great Western Highway Upgrade Program. This stage of the program proposes upgrades between Katoomba and Blackheath, and between Little Hartley and Lithgow. Planning and design for the Central section, between Blackheath and Little Hartley, is continuing and will be the subject of a separate business case.
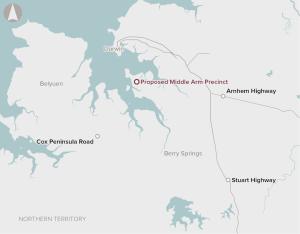
Recommended for investment to support the Northern Territory Government to advance planning and its business case to demonstrate how common user infrastructure will underpin industry development to create higher export value and economic diversification.
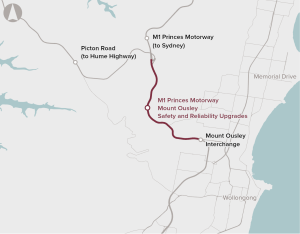
The section through Mount Ousley is a key corridor for movement of freight between the Illawarra region, Greater Metropolitan Sydney via the Princes and Hume Highways (via Picton Road), and southern Sydney industrial precincts such as Moorebank Intermodal Terminal.
The NSW Government, in partnership with local government, has identified strategic cycleway corridor networks for the Eastern Harbour City, Central River City and Western Parkland City. Robust prioritisation, staging, governance and delivery of these networks will be critical to realising this opportunity. This will need to be underpinned by close collaboration with local governments.
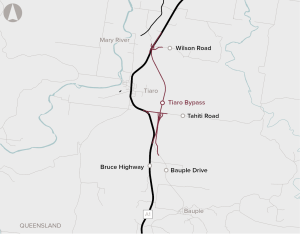
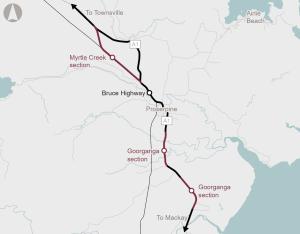
The Tiaro Bypass Project seeks to improve the efficiency, safety and resilience of the Bruce Highway through the development of a bypass to the east of Tiaro.

Recommended for investment to support the Northern Territory Government undertake planning activities to demonstrate the value of freight rail and logistics capacity improvements along the north-south Darwin-Tarcoola rail corridor to enable the export of renewable energy and low emissions commodities.
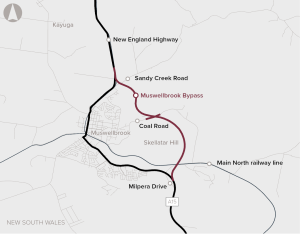
The Muswellbrook Bypass project aims to address existing problems through the development of a bypass of Muswellbrook to the east of the town and Skellatar Hill, starting near Milpera Drive and re-joining the New England Highway north of Sandy Creek Road.
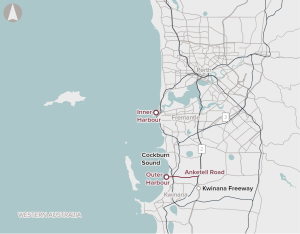
Investigation, planning, and potentially corridor and site preservation for additional container terminal capacity to accommodate future demand in Perth.

Recommended for investment to support the Western Australia Government undertake planning activities for the Westport program, to provide long-term supply chain capacity for future trade growth in the state.
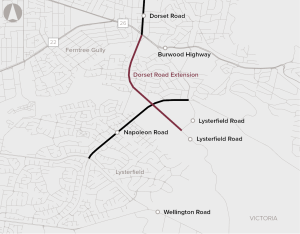
The Dorset Road Extension proposal involves the extension of Dorset Road from Burwood Highway to Lysterfield Road in south-eastern Melbourne, Victoria.
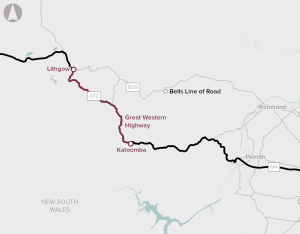
The proposal is to complete the duplication of the Great Western Highway. Over 100 km of the highway has been duplicated so far, leaving a 33 km gap between Katoomba and Lithgow.
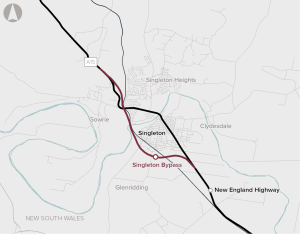
The New England Highway Singleton Bypass proposal aims to improve safety, travel times and travel variability for traffic on the New England Highway travelling through Singleton and will facilitate movement of heavy freight vehicles travelling on this section of the New England Highway.
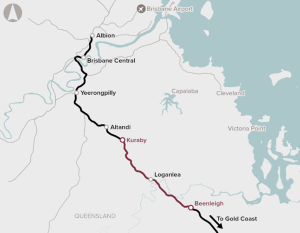
The Logan and Gold Coast Faster Rail (Kuraby to Beenleigh) proposal includes increasing rail capacity, modernised rail systems, upgraded train stations and road access, a new stabling facility, level crossing removals and a dedicated active transport facility.
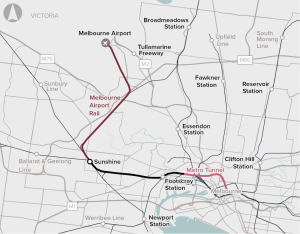
Melbourne Airport Rail will connect Melbourne Airport to Victoria’s metropolitan and regional rail network, delivering ‘turn-up-and-go’ train services from the airport to Melbourne’s CBD, via Sunshine.
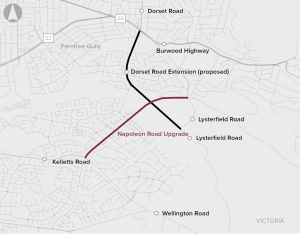
The Napoleon Road Upgrade proposal involves the duplication of Napoleon Road from Lysterfield Road to Kelletts Road in Rowville, in Melbourne's outer south-east.
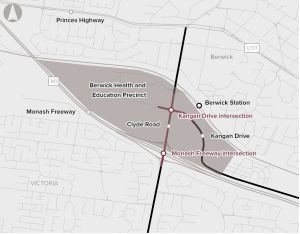
The Monash Roads Upgrade project involves the upgrade of two intersections within the Berwick Health and Education Precinct. It is expected to provide improved access to local employment and services, as well as reduced congestion and delays.
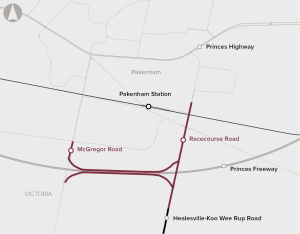
The Pakenham Roads Upgrade package is comprised of the McGregor Road Interchange Upgrade project and the Racecourse Road Upgrade project. The proposal includes duplication of Racecourse Road and upgrade of the McGregor Road and Racecourse Road freeway interchanges.
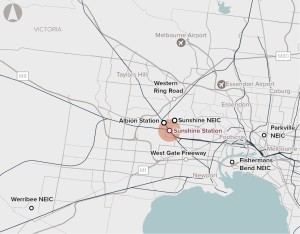
Opportunity to redevelop Sunshine Station and the surrounding precinct as a major future PT interchange linking Melbourne Airport, the CBD and regional Victoria.
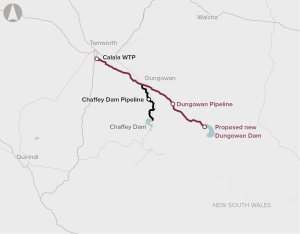
The Dungowan Dam and Pipeline is a proposal to increase town water supply for Tamworth and sustain the reliability of water for agriculture across the Peel Valley.
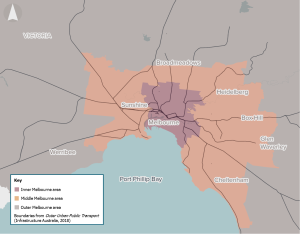
Melbourne’s monocentric urban form is constraining the economic potential of Melbourne’s middle and outer suburbs.
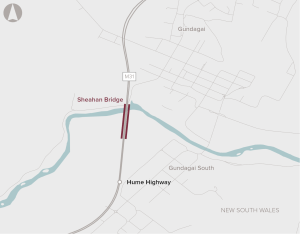
Strength limitations on the northbound Sheahan Bridge at Gundagai are constraining High Productivity Vehicle movements on the Hume Highway.
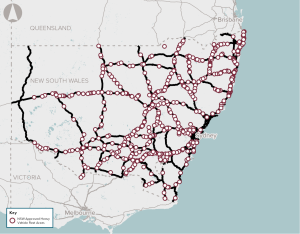
Insufficient or inadequate infrastructure to allow drivers of heavy vehicles to stop and rest across NSW.
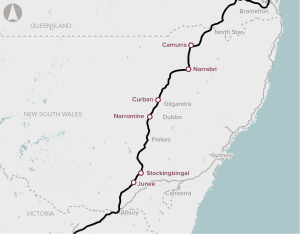
Ensuring interoperability between the Country Regional Network and Inland Rail to maximise productivity and efficiency of freight movements from regional NSW to domestic and export markets.
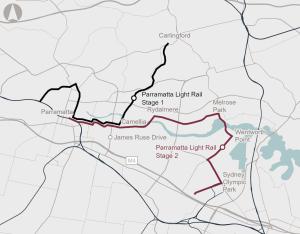
Recommended for investment to support the New South Wales Government to undertake planning and development activities for improving transport connectivity to support the growth of the Greater Parramatta and Olympic Peninsula precincts.
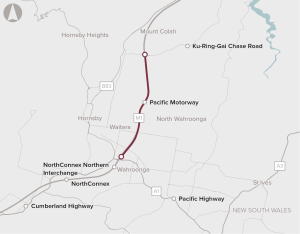
Extreme congestion on the M1 Pacific motorway between the existing North Connex portal and Mt Colah.
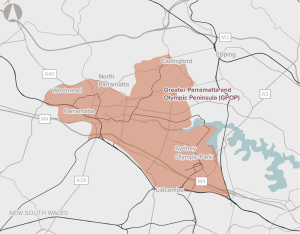
Opportunity to co-ordinate delivery of infrastructure to support sustainable growth in Greater Parramatta and the Olympic Peninsula.
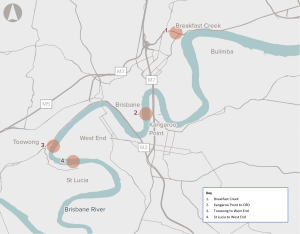
Opportunity to address challenges associated with congestion, forecast population growth and geographical limitations by improving active transport networks across the Brisbane River.
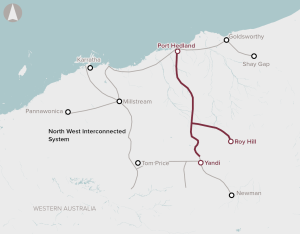
Limited energy transmission and storage infrastructure across the Pilbara in Western Australia.
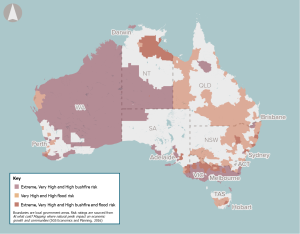
As the frequency and severity of natural disasters increase due to climate change, early warning systems present an opportunity to improve the safety and wellbeing of communities in high-risk zones.
During severe natural disasters, regional and remote communities are often isolated due to corridor closures on the National Land Transport Network (NLTN).

Existing intermodal terminals in SEQ are restricted in their ability to service Inland Rail trains (1800m long, double-stacked).
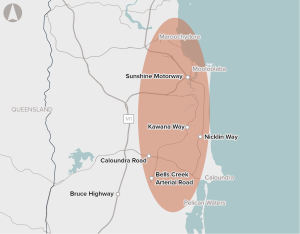
Strong population growth, a constrained road network, and limited transport options are contributing to congestion between Caloundra and Maroochydore.
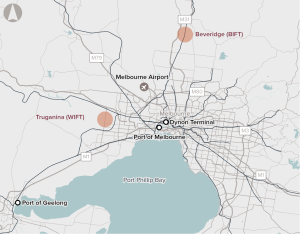
Existing intermodal terminal capacity in Melbourne is unable to service Inland Rail trains (1800m long, double-stacked).

Increasing coastal erosion and inundation risks across Western Australia.
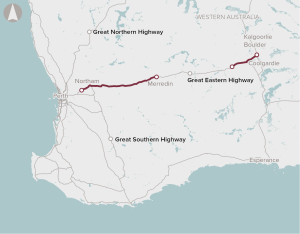
Deteriorating road conditions, increasing travel times, aging bridges and relatively high road maintenance costs on the Great Eastern Highway.
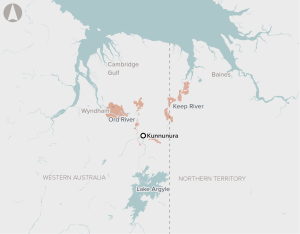
Opportunity to upgrade and extend irrigation channels to expand irrigated crops in the Ord River Irrigation Area in North-West Western Australia and the Keep River Plains in North-East Northern Territory.
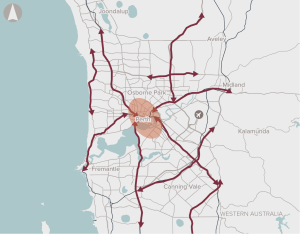
Worsening road congestion, high private vehicle use and a lack of dedicated active transport connections that link key strategic centres in Perth.
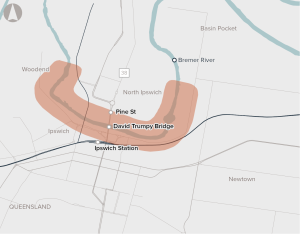
Strong forecast population growth and a single river crossing is expected to place increasing pressure on the transport network in Ipswich.
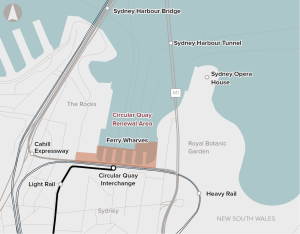
Recommended for investment to support the New South Wales Government’s revitalisation of the precinct to enhance accessibility and safety, improve transit capacity and connectivity and improve passenger and visitor experience.
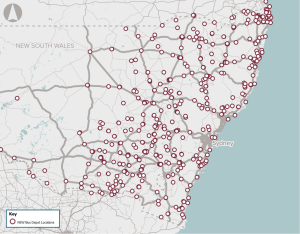
Recommended for investment to support the New South Wales Government undertake planning activities to define the infrastructure required to support the deployment of zero-emissions buses across the state.
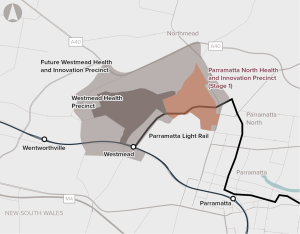
Opportunity to redevelop Government-owned land in Parramatta North, capitalising on the redevelopment of Westmead and the Parramatta Light Rail.

Greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and noise pollution associated with diesel-powered public buses in NSW.
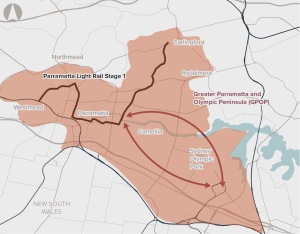
Poor connectivity to and from precincts in Greater Parramatta and the Olympic Peninsula, limiting ease of movement.
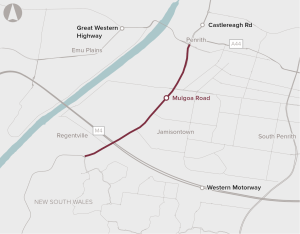
High levels of congestion and safety risks on Mulgoa Road in Western Sydney.
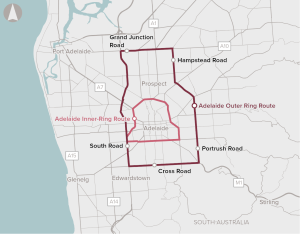
Increasing population growth in Adelaide is expected to increase congestion and travel times in the suburbs surrounding inner-Adelaide, to the CBD, as well as impact freight productivity and safety for pedestrians and cyclists.
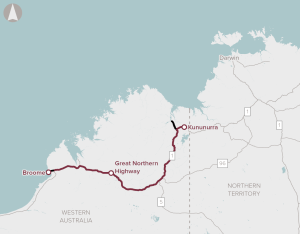
Recommended for investment to support the Western Australia Government to undertake planning activities for improving accessibility and highway safety, to facilitate economic growth and improved social outcomes.
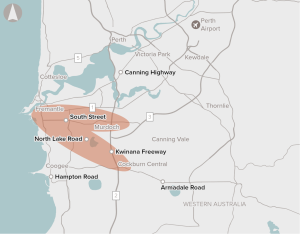
Limited high priority public transport services to connect employment centres and tourism hubs with major residential and commercial developments.
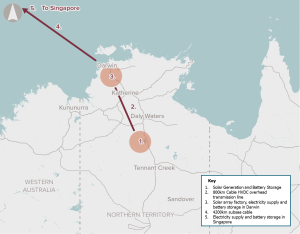
A proposal to supply renewable energy to Asia via a sub-sea cable
There is a significant opportunity to develop supply chains in Australia to meet potential demand in domestic and export markets.
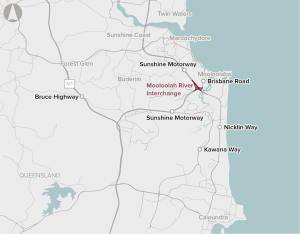
Traffic demand is exceeding the capacity of the Mooloolah River Interchange and the surrounding road network during peak periods.
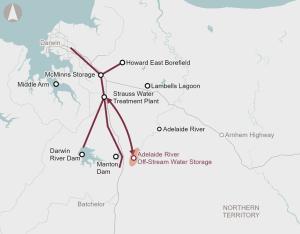
Recommended for investment to support the Northern Territory Government to undertake planning work to demonstrate how the Adelaide River Off-Stream Water Storage project can provide a water source necessary for the growth and prosperity of the territory beyond 2030.
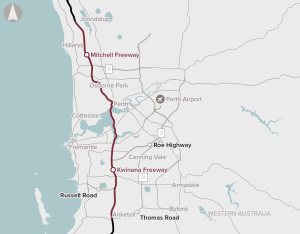
Widening the Mitchell and Kwinana Freeways and implementing Intelligent Transport System technologies.
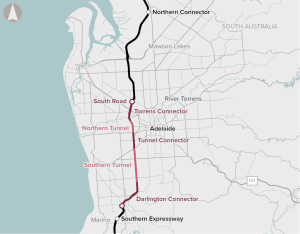
The North-South Corridor: Torrens to Darlington proposal is for the construction of a new 10.5 kilometre six-lane connection between the River Torrens and Darlington to complete Adelaide’s North-South Motorway. Tunnels make up over 60 per cent of the length of the proposed motorway connection.

The Coomera Connector Stage 1 proposal is for an alternative transport route to the M1 for local trips between Coomera and Nerang.
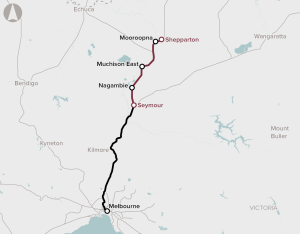
The Shepparton Line Upgrade (Shepparton Corridor Upgrade Stage 3) proposal is envisaged to deliver faster and more reliable services between Shepparton and Melbourne by providing track and signalling upgrades, and enhanced stabling.
There is limited provision of regional-level sporting facilities in the outer metropolitan areas of Perth, reflecting past undersupply that has not kept up with high population growth.

The proposal includes widening Tonkin Highway from four to six lanes and upgrading the intersections at Hale Road, Welshpool Road and Kelvin Road, providing benefits to north-south commuters and freight traffic around the Perth Airport Industrial Hub.
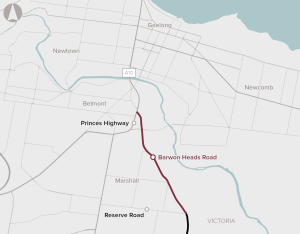
The Barwon Heads Road Duplication proposal seeks to duplicate a four kilometre section of Barwon Heads Road between Settlement Road and Reserve Road. The proposal includes construction of a new bridge over the rail line at Marshall and remove the level crossing, upgrade multiple intersections, a shared path, new street lighting and road signage.
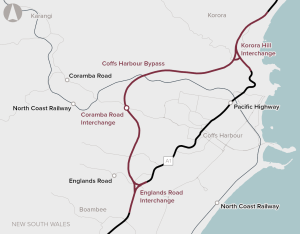
The Coffs Harbour Bypass proposal is for an upgrade of the Pacific Highway at Coffs Harbour. The proposal includes the construction of a new 12 kilometre bypass from south of the Englands Road intersection to Korora Hill and a 2 kilometre upgrade of the existing Pacific Highway between Korora Hill and Sapphire.
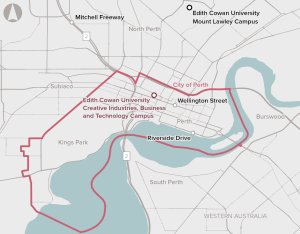
The Creative Industries, Business and Technology City Campus is a proposed new city campus in the Perth CBD.
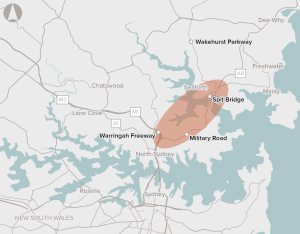
A motorway connection from the Warringah Freeway and the Gore Hill Freeway at Artarmon to Balgowlah and Killarney Heights, and an upgrade of the Wakehurst Parkway.
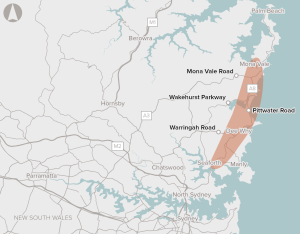
This proposal is specifically focused on the section of the A8 corridor between Seaforth and Mona Vale. Specific sections that have been identified for potential works include the Mona Vale complex, Narrabeen complex, Dee Why town centre, Brookvale Oval, and the intersection between Condamine Street and Pittwater Road.

The Tonkin Highway Extension proposal involves the construction of a 14 km extension of the Tonkin Highway from Thomas Road to the South Western Highway.
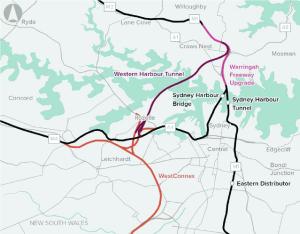
The Sydney Harbour Bridge and Sydney Harbour Tunnel are critical road links for Sydney’s transport system. Demand for these road links is expected to grow, increasing congestion.
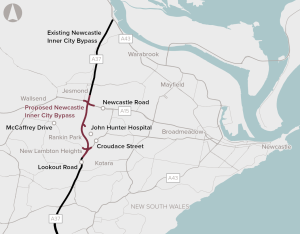
The Newcastle Inner City Bypass – Rankin Park to Jesmond project involves the construction of a 3.4 km section of the Newcastle Inner City Bypass. Bypassing the existing route is intended to reduce congestion and travel times, and improve road safety.

The Rockhampton Ring Road proposal is part of the Bruce Highway Upgrade Program. It is designed to provide an alternative to the existing section of the Bruce Highway through Rockhampton.
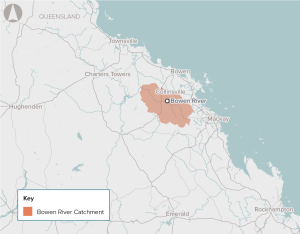
A constrained water supply is limiting the growth of agricultural, industrial and mining productivity in and adjacent to the Bowen Basin. Increasing the water supply can unlock additional agricultural land and facilitate a more robust water trading market with potential flow-on price reductions for mining and industrial water users.
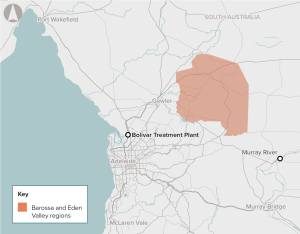
The River Murray is currently the major source of irrigation water to the Barossa Valley Region. Smaller volumes of groundwater are available, although the quality in some areas is not fit-for-purpose or sufficient to meet increasing industry demand.

The business case is for a new railway line to service Greater Western Sydney and the new Western Sydney Airport. It includes new stations at the Western Sydney Airport and the Western Sydney Aerotropolis, as well as fully-automated driverless trains.
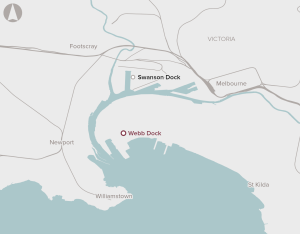
The number of containers handled by the Port of Melbourne is forecast to grow from 3 million twenty-foot equivalent container units (TEUs) in 2019 to close to 9 million TEU by 2050. The majority of this growth in containers will need to be delivered at Webb Dock. However, with the existing infrastructure, all freight to and from Webb Dock is carried by road. This results in increased congestion on the surrounding road network.